Kubernetes Previews
Deploy Kubernetes previews with enterprise-grade security and performance. Namespace's Kubernetes Previews enable development teams to test applications in isolated, ephemeral clusters that mirror production environments, accelerating feature development while maintaining operational standards.
Why Namespace Previews?
Getting Started
Create a preview cluster
-
Using the CLI, log into your workspace. If you're accessing Namespace from a cloud provider or your CI platform, we recommend to set up workflow federation instead.
$
nsc login -
Create a Kubernetes cluster to host your preview.
$ nsc create # Outputs the ID of the created cluster, e.g.: 072higp5dg0bg
Apply your Kubernetes configuration
-
Point your local
kubectlto the preview cluster.$ nsc kubeconfig write 072higp5dg0bg --output_to /path/kubeconfig.yaml $ export KUBECONFIG=/path/kubeconfig.yaml -
Deploy your application to the preview.
$
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
Expose your application
-
Expose a service of type LoadBalancer to wire access to your application.
$
kubectl expose pod nginx --type=LoadBalancer --port=80 -
Expose your service with Namespace.
$ nsc expose kubernetes 072higp5dg0bg --service=nginx --name=nginx-foobar \ --namespace=default Exported port 80 from default/nginx: https://nginx-foobar-072higp5dg0bg.ord2.namespaced.app
How it works
Namespace preview clusters build on Namespace Compute to deliver interactive access to a flexible, isolated test environment. When creating an instance, Namespace provisions a ready-to-use Kubernetes cluster in it and provides seamless access to the Kubernetes API. You can deploy and expose your applications using your existing tooling. Namespace will generate public, authenticated ingress URLs using managed TLS certificates, whether you use a Namespace-provided app domain, or employ custom domain configurations.
Namespace ingresses preserve original headers for application-level routing and support path-based and header-based routing within your application.
Kubernetes API access
Namespace previews provide full access to the Kubernetes API under test.
To configure your local kubectl client to access the remote test environment, use our CLI to produce and apply a kubeconfig.
$ nsc kubeconfig write <instance-id>
# Outputs the path of the produced kubeconfig, e.g.: /path/kubeconfig.yaml
$ export KUBECONFIG=/path/kubeconfig.yamlTo access the Kubernetes API without reconfiguring your local client, use the inline kubectl integration:
$nsc kubectl <instance-id> get pods,services
Monitoring and Debugging
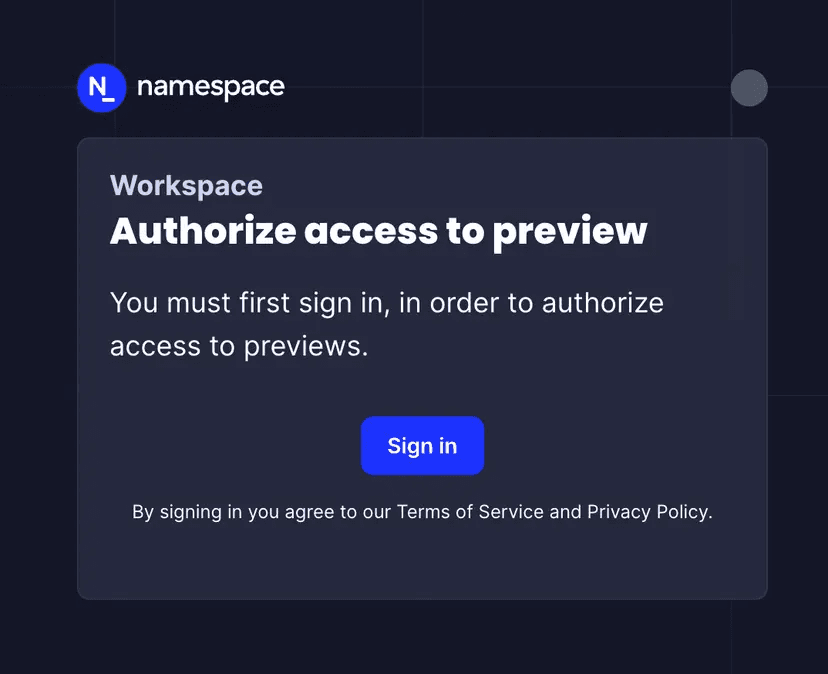
By building on Namespace Compute, you directly benefit from its comprehensive observability features providing deep insights into preview environment performance and behavior.
- Real-time Logging Access centralized logs from all pods, from the CLI or the Dashboard.
- Performance Monitoring Track resource utilization and network performance.
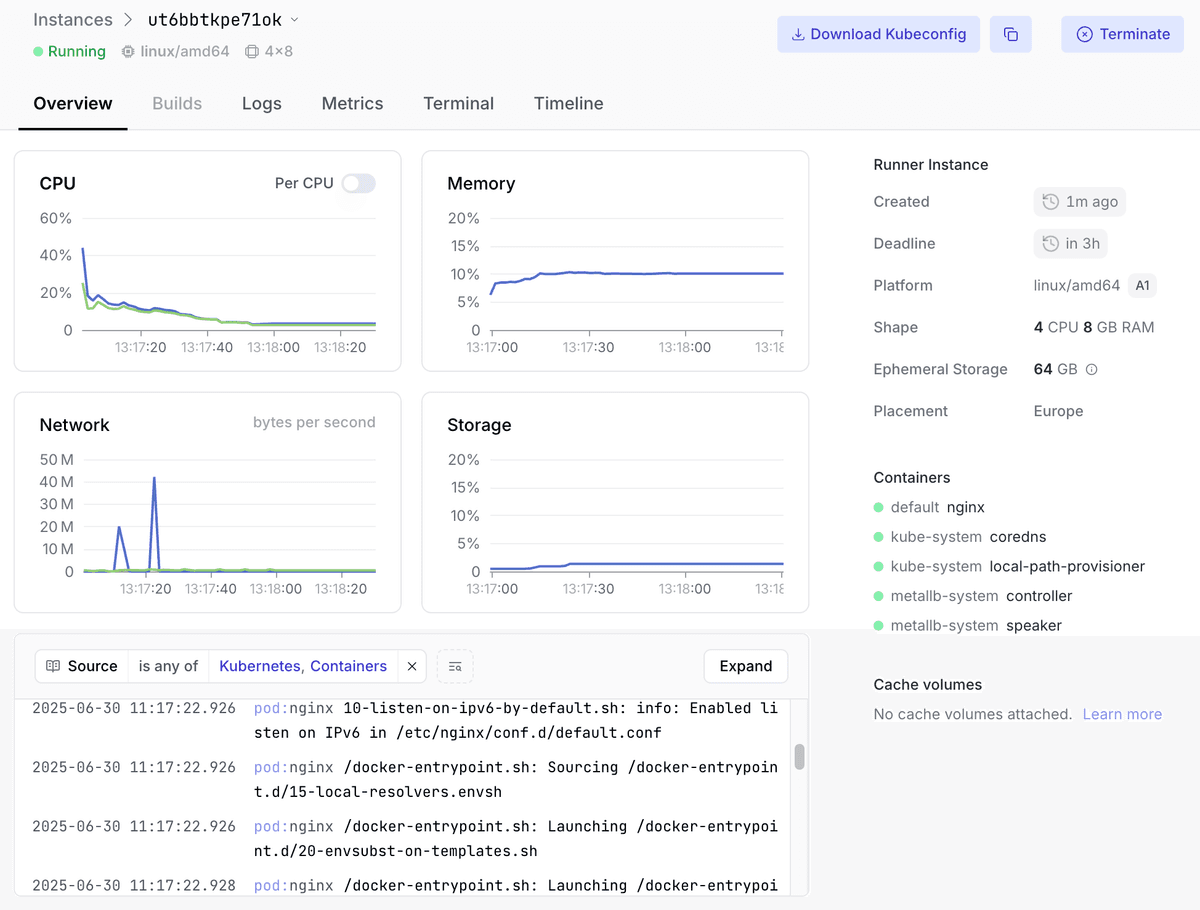
In case Kubernetes API access is not sufficient, Namespace also grants root SSH access to each instance, allowing you to inspect the underlying infrastructure powering the preview.
Wildcard Ingresses
For complex applications requiring multiple endpoints or dynamic routing, Namespace supports wildcard ingress configurations. Wildcard ingresses excel in scenarios requiring microservice architectures with dynamic service discovery and when testing API gateways managing multiple backend services.
Enable wildcard support
Create a cluster with wildcard ingress capability.
$nsc create --ingress wildcard
This outputs the ID of the created cluster, e.g.: 072higp5dg0bg
Deploy and expose your applications
$ nsc kubectl 072higp5dg0bg create deployment app --image=myapp:latest
$ nsc kubectl 072higp5dg0bg expose deployment app --type=LoadBalancer --port=80Configure a wildcard ingress
$ nsc expose kubernetes 072higp5dg0bg --service app --wildcard --port=80 \
--namespace=defaultAfter creating a wildcard ingress, all subdomain traffic is routed to your specified service:
*.<instance-id>.<region>.namespaced.appAutomatic Previews
Namespace's Kubernetes Ingress Manager automates preview creation through service annotations, eliminating manual exposure commands and integrating preview generation directly into your deployment pipeline.
Enable the ingress manager
Create a preview cluster, enable the ingress manager and point your local kubectl to it.
$ nsc create --features EXP_KUBERNETES_INGRESS_MANAGER
# Outputs the ID of the created cluster, e.g.: dr9flh12238uk
$ nsc kubeconfig write dr9flh12238uk --output_to /path/kubeconfig.yaml
$ export KUBECONFIG=/path/kubeconfig.yamlAnnotation-based service exposure
Control preview generation through Kubernetes service annotations:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: frontend
annotations:
kubernetes.namespace.so/expose: "true"
kubernetes.namespace.so/exposed-port-80: "ingress-name=my-app"
spec:
selector:
app: frontend
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: LoadBalancerVerify the exposed ingress
$ nsc ingress list dr9flh12238uk
https://my-app-80-dr9flh12238uk.ord2.namespaced.app (port: 80; default/frontend)Annotation Reference
| Annotation key | Valid values |
|---|---|
| kubernetes.namespace.so/expose Enable automatic preview generation. | Either true or false. |
| kubernetes.namespace.so/exposed-port-<port> Configure ingress options for specific port. | Comma-separated list using the following option:
|
Autoscaling Clusters
Namespace Kubernetes Previews can scale cluster resources based on workload demands, ensuring optimal performance while controlling costs.
Horizontal cluster scaling is performed automatically through a workspace-private network (VPC) as an increase in required resources is detected.
Note: Automatic cluster scaling is not enabled by default. Contact our support to get enrolled.